
How to Have Fun in the Sun According to RCCA’s Dermatologic Oncologists
East Coast residents are no strangers to winter weather, and those long, chilly months tend to make time under the summer sun that much more appealing.
HIPAA Alert: Potential Data Breach Learn More
Questions on Oncology, Hematology and/or Infusion Clinical Services due to COVID-19 Crisis – CALL 833-698-1623
Important Information for Our Patients Regarding the Coronavirus.
RCCA Providing Area Cancer Patients with Access to Care During Coronavirus Outbreak
RCCA Offering Patients Virtual Visits During Coronavirus Pandemic
Skin cancer, though dangerous, is highly treatable. The medical oncologists of Regional Cancer Care Associates (RCCA) have extensive experience treating melanoma and other forms of skin cancer. They use the latest evidence-based therapies to provide patients throughout New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and the Washington, D.C., area with compassionate and advanced care for skin cancer.
Skin cancer is caused by the irregular development and growth of skin cells. Skin cancer is relatively common in the United States. About 20% of people are diagnosed with some form of skin cancer by age 70.
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays via the sun or tanning beds greatly increases a person’s risk of skin cancer. Experiencing even a few sunburns, particularly those marked by blistering, can double the chances of developing skin cancer later in life. Other skin cancer risk factors include:
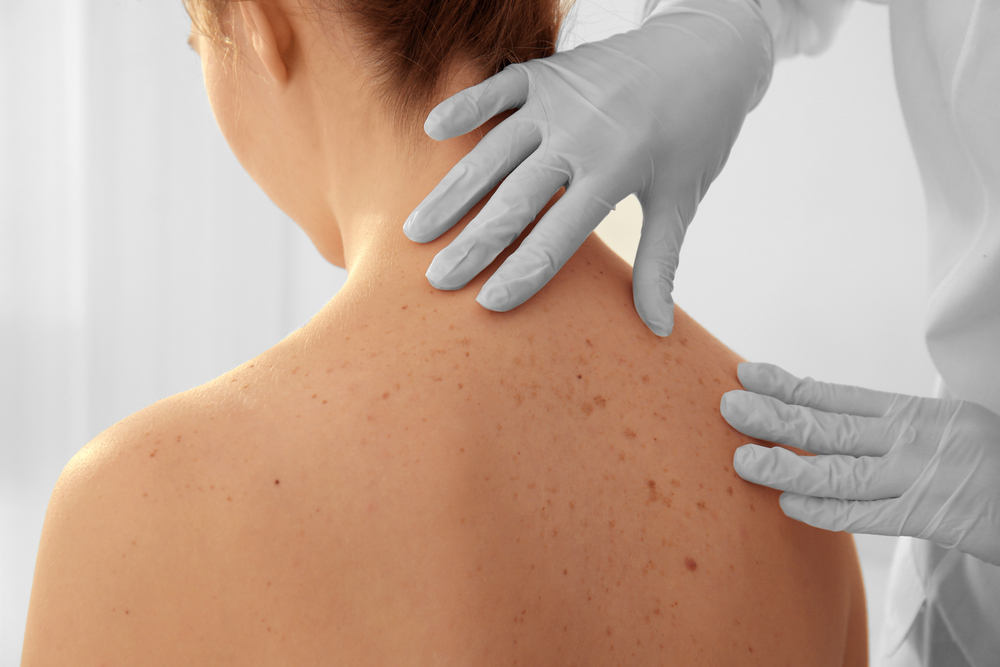
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends using the ABCDE method for skin cancer self-examinations. This approach is an acronym that stands for:
It is important to make a habit of reviewing the skin periodically to note any changes. If any of the following symptoms are noted during a self-examination, patients should see their primary care doctor or dermatologist for diagnosis and possible treatments:
Although these findings may not indicate the presence of a skin cancer, it’s best to have them checked by a medical professional.

There are two main types of skin cancer – carcinoma and melanoma – both of which are found within the skin’s epidermis, or top-most layer. The five types of carcinomas are:
Melanoma is the other main type of skin cancer. It originates in the melanocytes, cells located just below the basal skin cells. Melanocytes produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Although less than 1% of all skin cancers are melanomas, this is the deadliest form of skin cancer because of its tendency to spread to other vital organs.
Early treatment, is critical to the successful management of skin cancer. For example, among people diagnosed with melanoma – the deadliest of all skin cancers – the 5-year relative survival rate is 99% for those treated in the earliest stages of the disease.
Many factors come into play when deciding on the optimal treatment for any cancer. In the case of skin cancer, the options include:
The medical oncologists of Regional Cancer Care Associates have extensive experience and expertise treating melanoma and advanced forms of other types of skin cancer. For compassionate treatment for cancer or blood disorders, patients can visit one of RCCA’s many office locations across New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and the Washington, D.C., area or can request an appointment.
From empowering you with information and tools to fully understand skin cancer, to treating it quickly and comprehensively, RCCA is committed to your care. As one of the nation’s largest cancer physician networks, we have the reach, the resources and the localized accessibility to treat your very individualized needs with top-quality care and unfailing compassion.
For more information, or to schedule an appointment, call (844) 346-7222. You can also schedule an appointment by calling the RCCA location nearest you.

East Coast residents are no strangers to winter weather, and those long, chilly months tend to make time under the summer sun that much more appealing.
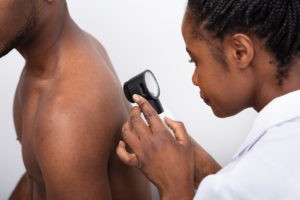
Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Share on email Share on print The New Jersey average of 22.2 new cases of melanoma
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with cancer, doctors can choose from many treatments to provide the best care possible for each
When standard cancer treatments aren’t providing the results you want, clinical trials may offer hope. Our physicians use clinical trials to study new treatments, helping transform cancer care for the better. You can enroll in a clinical trial to try groundbreaking treatment plans at zero cost to you.

Regional Cancer Care Associates is one of fewer than 200 medical practices in the country selected to participate in the Oncology Care Model (OCM); a recent Medicare initiative aimed at improving care coordination and access to and quality of care for Medicare beneficiaries undergoing chemotherapy treatment.